E-LINE Using VPWS on Cisco IOS: A Hands-On Lab Using EVE-NG
This guide walks you through building an E-LINE VPWS lab using Cisco IOS. Learn how to configure MPLS, LDP, and xconnect for point-to-point Ethernet services.
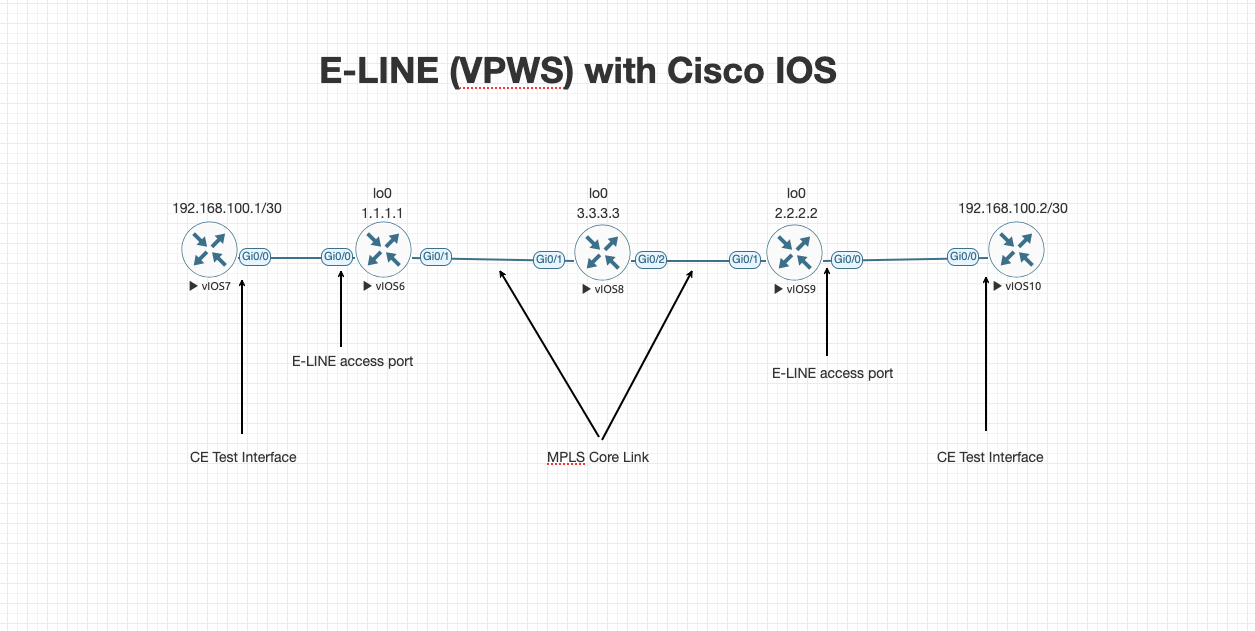
E-LINE is the MEF-standard name for a point-to-point Ethernet service. In Cisco IOS XR, it's implemented using VPWS (Virtual Private Wire Service) — a powerful way to simulate a virtual wire across your MPLS core.
🧠 What is VPWS?
VPWS (Virtual Private Wire Service) is a Layer 2 VPN technology that simulates a physical Ethernet connection between two customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network. It's used to build E-LINE services, providing raw Ethernet transport over MPLS.
Think of it as a virtual Ethernet cable that stretches between two locations, completely transparent to customer traffic.
🔧 Lab Overview: E-LINE (VPWS) on Cisco IOS
🔹 Topology:
CE1 --- PE1 --- P --- PE2 --- CE2
🔹 Technologies:
- Cisco IOS (IOSv or CSR1000v)
- MPLS + LDP
- OSPF for IGP
- VPWS using
xconnectwith MPLS encapsulation
📐 IP Address Plan
| Device | Interface | Connected To | IP Address | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE1 | Loopback0 | — | 1.1.1.1/32 | MPLS Router-ID |
| Gi0/1 | P Gi0/1 | 10.0.12.1/30 | MPLS Core Link | |
| Gi0/0 | CE1 Gi0/0 | — (L2) | E-LINE access port | |
| P | Loopback0 | — | 3.3.3.3/32 | MPLS Core ID |
| Gi0/1 | PE1 Gi0/1 | 10.0.12.2/30 | MPLS Core Link | |
| Gi0/2 | PE2 Gi0/1 | 10.0.23.1/30 | MPLS Core Link | |
| PE2 | Loopback0 | — | 2.2.2.2/32 | MPLS Router-ID |
| Gi0/1 | P Gi0/2 | 10.0.23.2/30 | MPLS Core Link | |
| Gi0/0 | CE2 Gi0/0 | — (L2) | E-LINE access port | |
| CE1 | Gi0/0 | PE1 Gi0/0 | 192.168.100.1/30 | CE Test Interface |
| CE2 | Gi0/0 | PE2 Gi0/0 | 192.168.100.2/30 | CE Test Interface |
Note: No IPs on CE-facing interfaces — it's pure Layer 2 transport.
⚙️ Router Config Snippets
PE1 (IOS)
hostname PE1
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
interface Gi0/1
ip address 10.0.12.1 255.255.255.252
mpls ip
no shut
interface Gi0/0
no ip address
xconnect 2.2.2.2 100 encapsulation mpls
no shut
mpls label protocol ldp
mpls ip
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0PE2 (IOS)
hostname PE2
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
interface Gi0/1
ip address 10.0.23.2 255.255.255.252
mpls ip
no shut
interface Gi0/0
no ip address
xconnect 1.1.1.1 100 encapsulation mpls
no shut
mpls label protocol ldp
mpls ip
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0P Router (Core)
hostname P
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
interface Gi0/1
ip address 10.0.12.2 255.255.255.252
mpls ip
no shut
interface Gi0/2
ip address 10.0.23.1 255.255.255.252
mpls ip
no shut
mpls ip
mpls label protocol ldp
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.0.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0🧪 CE Device Configuration
In this lab, we're using two CE routers (CE1 and CE2) to simulate customer edge devices connected to the service provider's E-LINE (VPWS) service.
You can assign simple IP addresses on each CE interface to verify that the Layer 2 service is functioning properly. These IPs are not part of the service provider core, and are only used for test traffic.
CE1 Gi0/0/0/0: 192.168.100.1/30
CE2 Gi0/0/0/0: 192.168.100.2/30
ping 192.168.100.2 # from CE1
If the ping is successful, your E-LINE service is working!
🔍 Verification Commands
show xconnect all
show mpls l2transport vc
show mpls forwarding
📚 VPWS vs E-LINE — Same Thing?
Yes! In MEF language:
| MEF Service | Cisco Term |
|---|---|
| E-LINE | VPWS |
E-LINE = Point-to-Point Ethernet Service
VPWS = How Cisco implements it using MPLS
🔚 Conclusion
This is just a small lab to freshen up, learn more, or just stay busy. Whether you're brushing off the rust or exploring service provider tech, it's a great practical challenge.
💡 Personal Note:
I actually ended up doing this lab twice because I couldn’t get CE-to-CE ping working the first time. After exhausting every bit of troubleshooting logic and confirming the configs were solid, I finally determined it was an environment issue inside EVE-NG. Deleting and reloading all the nodes fixed it immediately.
So if you're stuck and everything looks right — don't rule out your environment!
You've now built an E-LINE/VPWS lab using Cisco IOS — leveraging MPLS, LDP, and xconnect pseudowires for Layer 2 Ethernet services.
Next steps? Upgrade to VPLS, try EVPN, or test redundant pseudowires with backup neighbors. We shall see.
Let the labbing continue 🚀
— Bryan Steele 🧠⚙️

